Container Gardening with Children: Botany, Responsibility, Food Preparation, and Compassion
If you’re an avid gardener, you’ve likely already started your seeds and planned out your raised beds. You know the sweet reward of eating a sunshine-warmed tomato in the middle of summer, and you’ve seen the many benefits for you and your family that extend far beyond the tasty produce.
But if you don’t consider yourself a green thumb? Curious but never felt like you had the time? Are extensive beds not an option for you? Or would you rather start small before committing to anything large? Regardless of the reason, container gardening is an excellent option for everyone. A container garden can be as simple as a single potted marigold on the porch, vegetables, fruits, herbs, and flowers taking over every possible square inch of your outdoor space, or (most likely) something in between.
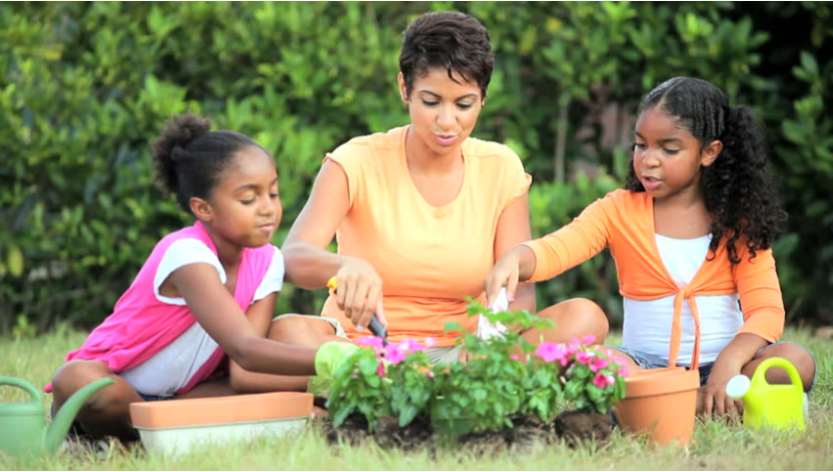
Growing a container garden with your children is simpler than you might think, and it’s an enriching experience that will give them skills to last a lifetime. Check out this video for some inspiration:
Expanding Upon the Botany Curriculum
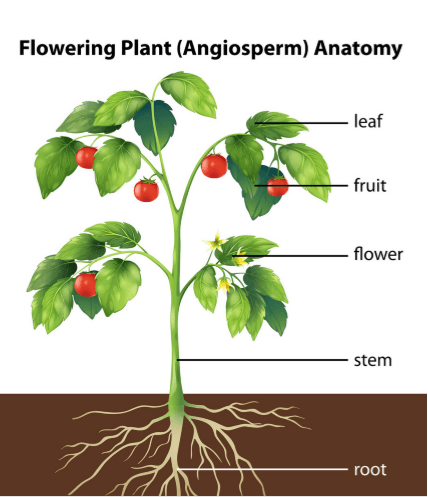
All Montessori classrooms infuse botany into the environment, lessons, and work options. By starting a container garden you are making an authentic bridge between home and school. Your child will have hands-on experiences that will bring skills to life, building on their prior knowledge and giving them even more. Interested in making direct connections to the Montessori botany curriculum? Here are some tips:
- Point out and name the parts of plants.
- Help your child learn to identify various plants.
- Discuss what plants need to survive and how you can help your plants meet those needs.
- Compare different leaf shapes.
- Talk about plant attributes: annuals versus perennials, vine growth form versus herbaceous, or how individual plants change over time.
- Make math connections: make predictions, take measurements, collect and chart data.
- Teach your child about how plants reproduce, and make connections with the organisms that assist in the process.
Nurturing Responsibility
It may seem obvious, but having a garden (no matter how small) is a great way to teach your child about responsibility. Caring or not caring for plants produces natural consequences in the purest form. If your plants are consistently watered, weeded, and given the correct amount of sunlight, chances are they will flourish and produce beautiful results. Neglected plants, however, and likely to shrivel up and die rather quickly.
It would be totally normal for your child to show excitement and enthusiasm when you first begin gardening. After a week or two, their desire to participate is likely to wane. Use this as an opportunity to talk about what responsibility means. Let them know that the plants are counting on their help to stay alive. Develop structures that will help your child be successful: this could be as simple as daily verbal reminders to water the plants, or you could have a chart on the wall for them to refer to. It goes without saying, but the level of independence we can expect depends largely on their developmental plane.
Building Opportunity for Food Preparation
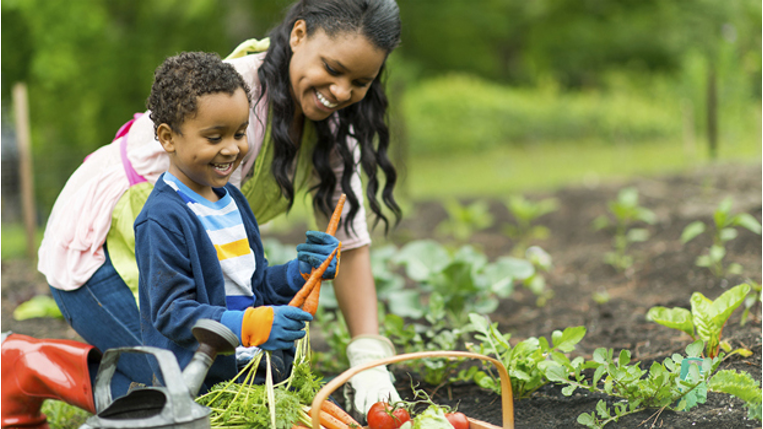
In a Montessori primary environment, food preparation is a part of the daily routine. Children learn to spread, slice, mix, and create simple snacks for themselves and others. Even in the older grades, many Montessori schools find ways to bring food preparation into their work. This may take the form of preparing lunch for one another, creating birthday walk snacks, or trying various cultural recipes for different world celebrations.
Growing your own food, even if it’s just a few cucumbers, gives your child a chance to extend their food preparation work at home. By learning to create snacks and meals, they are building one of the most critical life skills we can give them. Not only does this create a sense of self-sufficiency, it also gives children an opportunity to care for the other people in their family. Preparing and sharing food together strengthens bonds (and it’s so much tastier if you have grown the food yourself!)
Cultivating Compassion
For those of us who love Montessori, supporting the growth of the whole child is so much more important than focusing on academics alone. Do our kids need to learn to add and read? Of course they do. They also need to learn how to be kind human beings. The best way to teach this is to make sure they are surrounded by patient and supportive adults who model their best.
Another wonderful way to cultivate compassion is to teach your child the importance of caring for another living thing. Pets are one common way families try this, but caring for plants is another. Over time, even young children will begin to understand that a living organism depends on them.
Have you heard that plants may react positively to certain sounds, including classical music and human voices?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=auA7cEUzPQI
If you have been debating whether or not to start gardening with your child, we hope this video has given you the courage to try it out! We can’t wait to hear how it goes.
You might also like